Two men were running through the jungle chased by a lion. One of them stopped, took off his backpack and took his trainers out. The other man turned around. “Why are you putting your trainers on?” he asked, “They won’t make you run faster than the lion”. To which the man replied “I don’t need to run faster than the lion…”
In the current market conditions just blindly running won’t get you ahead of your competitors. And standing still is not a sustainable option. Those that succeed won’t be the ones that batten down the hatches and retreat to the trenches, history shows it will be those that continue to innovate and cultivate ideas. During the 1990-91 recession, according to a Bain & Company study, twice as many companies leaped from the bottom of their industries to the top as did so in the years before and after.
“Even though we’re in an economic downturn, we’re in an innovation upturn” said Bill Gates at the time.
In the 1920’s Post and Kellogg’s went into the recession head to head. Post cut back, it reined in expenses and slashed advertising budget. Kelloggs meanwhile maintained their marketing spend and pushed their newly launched product, Rice Krispies. Today Kellogg’s are a household name. Where are Post?
IT organisations are retreating to core, keeping the lights on and holding off any “non-essential’ projects, innovation included. This is a shortsighted viewpoint, but not entirely unexpected. With project life cycles taking so long, innovation traditionally takes significant investment and time to see results. Modern lean and agile approaches to IT are a challenge to this entrenched view. It is possible to innovate at speed. It is possible to take an idea and turn it into something tangible in weeks rather than years. Let’s start with the idea. Where does it come from? You could get the brightest minds from expensive management consultancy firms, but they take time. And in uncertain times, what do they really know? (I speak with experience having once been a customer strategy management consultant). Alternatively you could harvest ideas from your customers. That’s what IdeaStorm does for Dell. And Mix does for Oracle (built by ThoughtWorks by the way). Don’t restrict this to your customers, building an internal ideas engine in the enterprise yields great results.
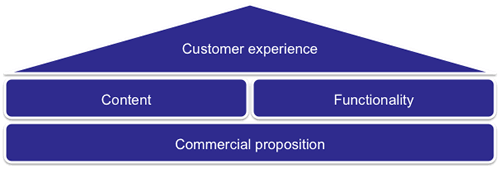
So once you’ve got the idea, how do you nurture it from a vision into a proposition that has legs?
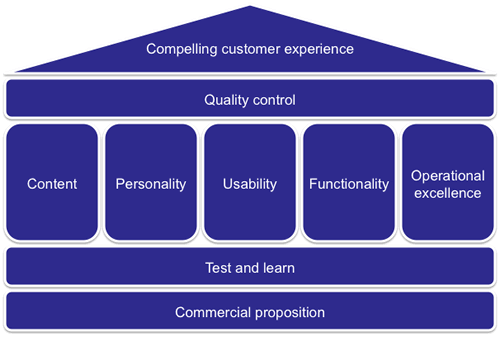
Product innovation is all very well, but do you have the capability and the attitude to really do it? In the current ecomomic climate, unless product innovation is in your DNA, chances are it will need to be accompanied by process innovation. Why? Because most organisational processes are slow, cumbersome and hinder the agility required to really innovate.
In 2009, if there’s one thing that organizations need, it’s agility. Our economy and the business environment are a steady stream of ups, downs and rapid change; in such an environment, the ability to sense, respond and react are true survival skills!
At ThoughtWorks we do both these things for our clients all the time, helping them introduce aligity into the whole product development lifecycle; product innovation through process innovation. It starts with helping them rapidly distill their vision into something concrete, then prirotising and estimating what is important before building it at speed with quality to get innovation to market; fail fast or succeed sooner.
Recession doesn’t make the market need disappear. Andrew Rezeghi in this great paper (which is abound with stories of companies who have innovated through recession) argues you should invest in your customers, now they need you most, loyalty hangs in the balance. Whilst the market may be driving down prices, now is the time to focus on experience based differentiation. How can you use digital channels to engage with your customers in new and compelling ways? How can you harness social media and new interaction paradigms to delight and engage your customers? Ho can you innovate at speed? Go beyond your product and grow roots for lifetime value when the good times return.